

Kerberos developers set out to provide a network authentication protocol that could be used to authenticate trusted hosts communicating over untrusted networks. Attackers with access to the network could easily eavesdrop on network transmissions, intercept user IDs and passwords, and then attempt to access systems for which they were not authorized. Systems routinely transmitted passwords "in the clear," meaning unencrypted. It also enabled those users to be authorized to access those systems.Īt that time, networked systems typically authenticated users with a user ID and password combination. The original objective of Kerberos was to provide a way for users of the MIT network to securely authenticate themselves to the systems they needed to use. What does the Kerberos authentication protocol do? In 2013, the consortium was expanded and renamed the MIT Kerberos and Internet Trust Consortium. In 2005, the Internet Engineering Task Force published the Kerberos protocol as a Proposed Standard in Request for Comments 4120. The MIT Kerberos Consortium was founded in September 2007 to further the development of the technology. Version 5 of the protocol - the current version - was first published in 1993. Work on Kerberos began in the late 1980s. It also protects messages from eavesdropping and replay attacks. Kerberos authentication uses conventional shared secret cryptography to prevent packets traveling across the network from being read or changed. KDC " tickets" provide mutual authentication, allowing nodes to prove their identity to one another in a secure manner.

It runs as a single process and provides two services: an authentication service and a ticket granting service (TGS).
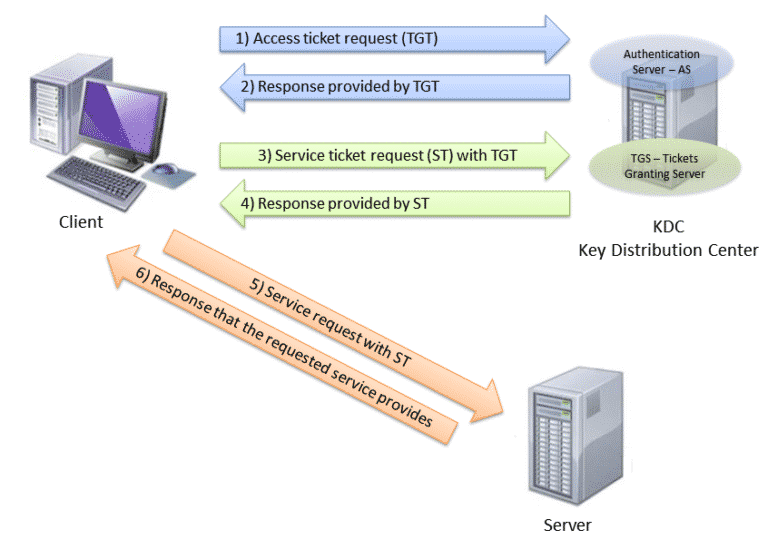
Users, systems and services using Kerberos need only trust the KDC. a key distribution center (KDC), which acts as Kerberos' trusted third-party authentication service.the network resource, which is the application server that provides access to the network resource and.The three heads of the Kerberos protocol represent the following: The name was taken from Greek mythology Kerberos (Cerberus) was a three-headed dog who guarded the gates of Hades. Kerberos was developed for Project Athena at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Broadband service providers also use the protocol to authenticate cable modems and set-top boxes accessing their networks. Since Windows 2000, Microsoft has used the Kerberos protocol as the default authentication method in Windows, and it is an integral part of the Windows Active Directory ( AD) service. Kerberos support is built in to all major computer operating systems, including Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS, FreeBSD and Linux. Kerberos is a protocol for authenticating service requests between trusted hosts across an untrusted network, such as the internet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
